You can assign a disk safe to a volume. In this case, the volume must exist before before the disk safe.
Use the following steps to add a volume to Server Backup Manager.
To add a volume:
- In the Main menu, click Volumes, and then click Create New Volume in the Volumes menu. Server Backup Manager displays the Create New Volume window as shown in the following image.
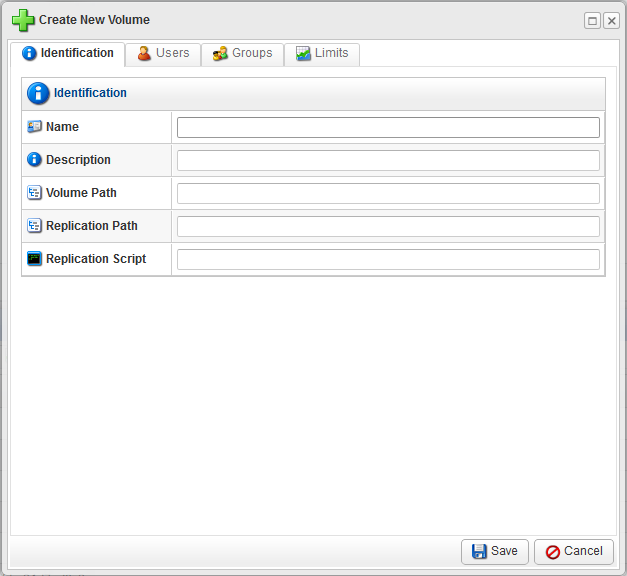
- Define the new volume properties.
- Identification. This tab allows you to identify the volume.
- Name. Volume name used to identify the volume within the system.
- Description. Additional information used to describe the volume. SBM displays the description in the Volumes list.
- Volume Path. The path for a new or existing folder. Any assigned disk safes are placed in this folder.
- Replication Path. The path for disk safe replication in this volume. For example, the Volume Path is /mnt/sdb1/ext4 and the Replication Path is /mnt/sdb1/ext4-R.
- Replication Script. Script used to create the replication.
- Users. This tab allows you to assign users to the volume.

Note
After upgrading, existing Sub-User assignments will not be removed.- To add a user to the volume, select the appropriate user name from the list, and then click Add. Click the red X icon to delete a user account from the volume.
- Groups. This tab allows you to assign groups to the volume.
- To add a group to the volume, select the appropriate group name from the list, and then click Add. Click the red X icon to delete a group from the volume.
- Limits. This tab allows you to set options regarding file excludes, recovery point archiving, and control panels. You can define limits replication, recovery points, and archive points.

Note
When you set a limit for a volume, it is enforced to all disk safes and policies assigned to that volume. For example, if a volume limits replication frequency to daily, you cannot have hourly disk safe replication. The same rule applies to retention policy, quotas, allowing file excludes, etc. - Allow File Excludes. Check this option to activate the File Excludes feature for all the disk safes assigned to that volume. If you check this option, then the system allows you to specify any files and folders that you do not want backed up during the replication policy. By default, all file and folders from the selected devices are replicated. Read more in About exclusions and Exclude files and folders.
- Allow Recovery Point Archiving. Check this option to activate the Archiving feature for all the disk safes assigned to that volume. If you check this option, the system allows you to create archives of your data on a specified hour, day, week, or month. If the option is enabled, then you can specify the Archive Point Limit. Read more in Manage archiving.
- Allow Control Panels. Check this option to activate the Control Panels feature for that volume. If you check this option, the system allows you to back up and restore hosting control panel user accounts. Read more in Hosting control panels.

Tip
There is a system-wide option to enable the Hosting Control Panels feature (Configuration Product features "Enable Hosting Control Panels" option under "Hosting Control Panels"). Read more in Enable the Hosting Control Panels feature. - Allow Database Backups. Check this option to activate the Database feature for that volume. If this option is checked, the system allows you to back up and restore such databases as SQL, Exchange, and MySQL. Read more in Protect SQL Server, Protect Exchange, and Protect MySQL.

Note
Note that all these 4 (four) check boxes are checked by default. - Replication Limit. This option defines the lowest replication frequency for all the disk safes assigned to that volume. For example, if you set the volume replication limit to Weekly, then the minimal replication frequency for the disk safes in that volume are weekly. Hourly and daily replications are restricted.
- Data Retention. Here you can set the limits for Recovery and Archive Points stored in all of the Disk Safes assigned to the Volume. When the combined number of Recovery/Archive Points in all of the Disk Safes exceeds the defined limits, the old Recovery/Archive Points will be merged. See Merge recovery points.
- Identification. This tab allows you to identify the volume.
- Recovery Point Limit - Specify the maximum number of Recovery Points that can be stored in the Disk Safes assigned to the Volume.
- Archive Point Limit - Specify the maximum number of Archive Points that can be stored in the Disk Safes assigned to the Volume. The option is available if the "Allow Recovery Point Archiving" option is enabled under "Option."
Quotas
Quotas are set to limit the disk usage of the Volume. The limit is set for all Disk Safes in the Volume on the basis of space occupied by Disk Safes, size of deltas, or number of deltas.
| Tip You can define Disk Quotas in Configuration. See Configure Manager Options. |
- Quota Type - From the drop-down menu, select a quota type:
- On Disk Size - Quota is based on the raw Disk file size of all the Disk Safes and their files in the Volume's folder.
- Size of Deltas in Disk Safe - The quotas will calculate the sum of the sizes (after compression) of the actual block level deltas in the Disk Safe file. Disk Safe's overhead and unused space in the Disk Safe file are not counted against the quota. You can find a description of deltas in Manage Disk Safes.

Note
Similar to a database, the Disk Safe format adds overhead to the raw data. This can happen if you delete more deltas from the Disk Safe than you add. For example, you delete a large number of data from the data set you are protecting. That data are no longer retained in any of your Recovery Points. As old Recovery Points are merged out and block-level deltas are no longer needed, they are "freed" from the Disk Safe file. Until there is a vacuum of the Disk, the size of the Disk Safe .db file(s) will not get smaller. You can run vacuuming but it is time consuming, causes internal fragmentation of the .db Disk Safe files, and can affect the files' performance.
- Soft Quota - The value in bytes or in deltas. Soft Quota is a warning level where users are informed they are close to reaching their effective limit.
- Hard Quota - The value in bytes or in deltas. Hard Quota allows resources to be occupied by data. If the Hard Quota is reached, then the system forbids generating new Recovery Points. The replication is interrupted and failed.
5. Once the Volume settings are specified, click Save to add the new volume to the system. SBM displays the volume in the list.
Labels:
None
