1. Create a Recovery Database
To recover mailboxes, create a recovery database as described below.
1. Launch the Exchange Management Shell to restore the mailbox. Go to Start > (All) Programs > Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 Exchange Management Shell.
2. The Exchange Management Shell screen will open.
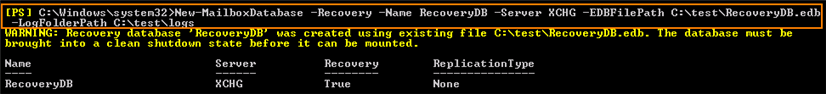
3. Use the New-MailboxDatabase command to create a mailbox database object in the database container in the Active Directory. For detailed syntax and parameter information, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997976(v=EXCHG.140).aspx.
In our example, we restore the C:\test\RecoveryDB.edb file using the following command:
2. Use Server Backup Restore
Use Server Backup to restore a Microsoft Exchange 2010 Mailbox to an alternate location. See details in Restoring a Microsoft Exchange 2010 Database to an Alternate Location.
| Notice Use the database created above to map against the Recovery Point Exchange database. |
3. Mount the Recovery Database
Mount the database if it was not already mounted by the Server Backup alternate restore.
To mount "RecoveryDB," use the Mount-Database command. For detailed syntax and parameter information, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa998871(v=EXCHG.140).aspx. In our example, we use the following command:

1. Use the Get-MailboxStatistics command to obtain information about a mailbox, such as the size of the mailbox, the number of messages it contains, and the last time it was accessed. For detailed syntax and parameter information, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb124612%28ru-ru,EXCHG.140%29.aspx.
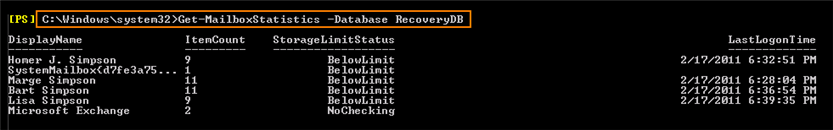
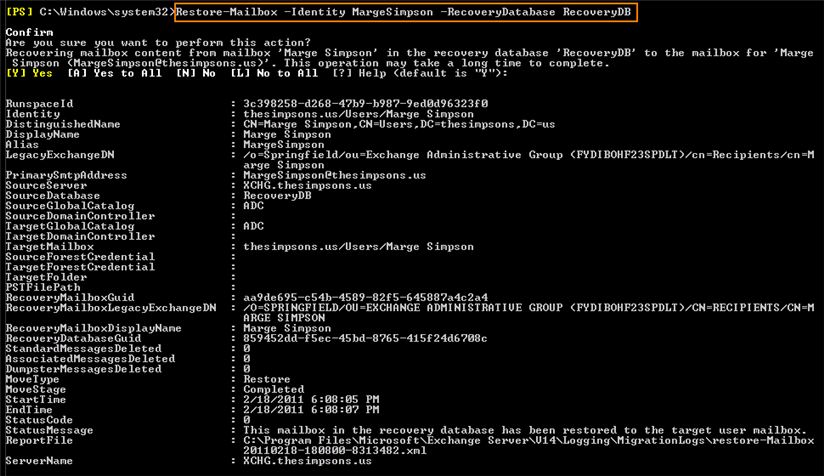
2. Extract mailbox content from a restored database using the "Restore-Mailbox" command. The -RecoveryDatabase parameter specifies the recovery database from which you are restoring the mailbox. In the following example, we restore a "MargeSimpson" mailbox. More parameters for "Restore-Mailbox" can be found here: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb125218.aspx