R1Soft CDP Server uses the Virtual Full Backup method. First, the initial full backup (Initial Replica) is created. After that, each time a replication is performed, it stores only the differences (block-level deltas) since the last replication.
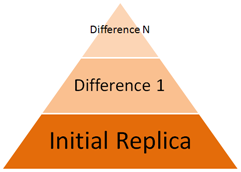
Each replication creates a point-in-time image of the Device, it is called a Recovery Point. To map the block versions and Recovery Points, the block deltas database is used. This database is a Disk Safe.

A Disk Safe is used to keep and arrange the pieces of replicated information. You can define a Disk Safe as a container for data needed for a restore.
| Tip You can restore from any available Recovery Point in any Disk Safe. |
Disk Safes have assigned Device(s) selected for backup. One Device can be assigned to multiple Disk Safes.
| Notice You cannot start backing up a Device until there is a Disk Safe to which this Device has to be backed up. |
To run a replication, you need to associate a Data Protection Policy with your Disk Safe. The Policy will back up the Disk Safe's associated Device(s).
| Tip You can exclude folders/files from the replication while defining the Policy's properties. |
On a physical level, Disk Safe is a directory containing:
- .db file
- .db-journal file
- metadata folder
Disk Safe Properties
Disk Safes have the following properties defined during Disk Safe creation:
- Identification - Unique name to distinuguish the Disk Safe in the list and while defining policies.
- Disk Safe Location - Location where the Disk Safe folder is physically saved.
- Compression Type - Using compression helps to reduce the consumption of hard disk space or transmission bandwidth.
- Devices - You can assign one or several hard Disks, Partitions, and other Volumes of a Host where file systems are mounted as Devices.
These characteristics, except Disk Safe Location, can be changed for an existing Disk Safe via CDP Server Interface.
In addition to the above properties, the following properties are available for the existing Disk Safes:
- Enabled
- Recovery Points
- Size
Disk Safe States
Disk Safes can be in one (1) of the following states:
- Opened - You can associate tasks including Backup with opened Disk Safes, and browse its Recovery Points.
- Closed - Closing a Disk Safe prevents any tasks associated with it from running, and you will not be able to browse the Recovery Points contained within the Disk Safe.
Available Disk Safes Actions
- Create new Disk Safes.
- Edit properties of existing Disk Safes.
- Attach(open) existing Disk Safes to the system.
- Close (disable) Disk Safes.
- Detach Disk Safes.
- Delete Disk Safe and all its data.
- Vacuum Disk Safe.
- Browse Recovery Points contained within the Disk Safes.
- Move Disk Safe from one location to another on a CDP Server.
- Copy Disk Safes from one CDP Server to another.
- Copy Disk Safes across Windows/Linux platforms.

Tip
Tools like Windows Explorer drag-and-drop, scp, xcopy, ftp, etc. can be used to move Disk Safes.



